Blog
How Precise Structural Design Optimization Reduces Steel Consumption in PEB
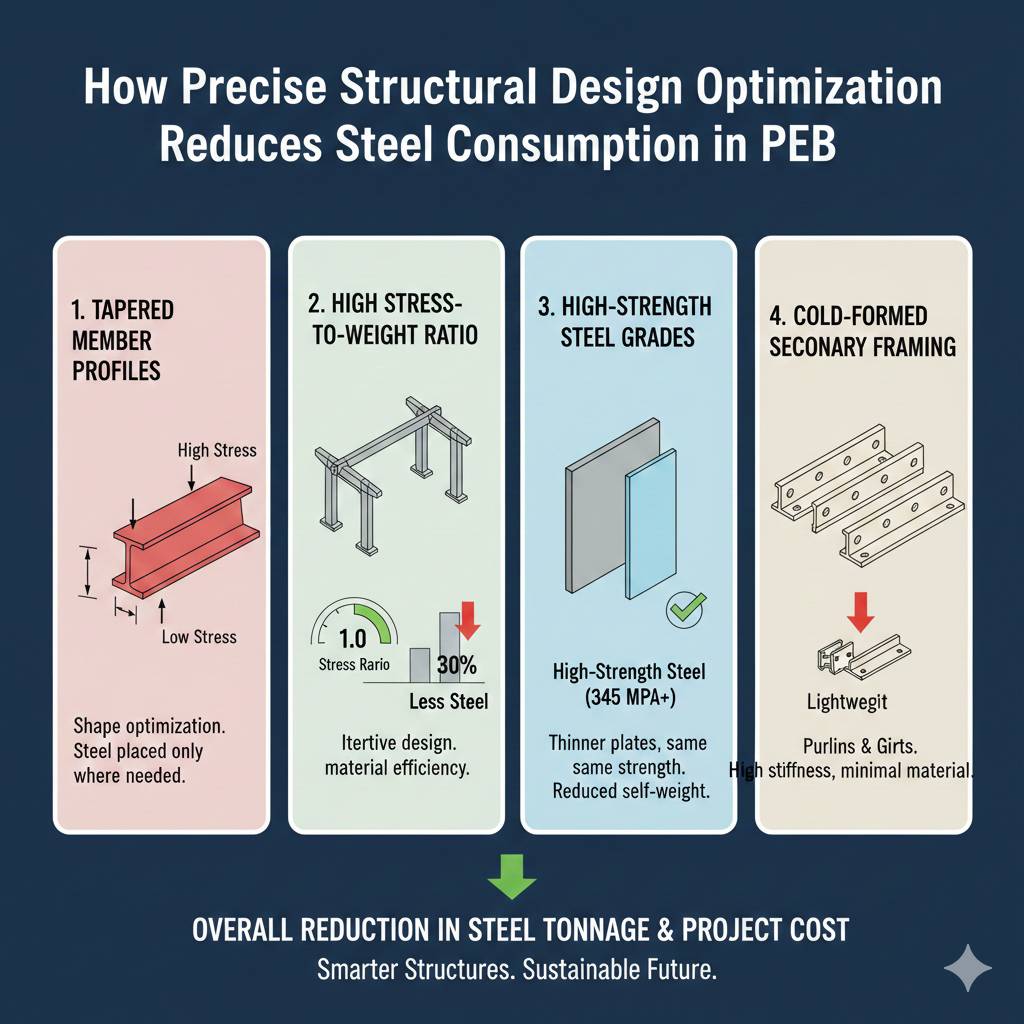
In steel construction, especially in Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEB), the difference between an average design and an optimized design is often measured not in millimeters—but in tons of steel.
Steel is one of the most expensive and carbon-intensive materials used in construction. As project costs rise and sustainability becomes a priority, precise structural design optimization has emerged as one of the most powerful tools to reduce steel consumption—without compromising safety or performance.
At Rakhra Associates – Structural Engineers in Chandigarh, optimization is treated as a core engineering responsibility, not an optional enhancement. This blog explains how structural optimization works in PEB systems, why it reduces steel usage, and what engineering decisions truly make the difference.
Understanding Steel Consumption in PEB Structures
Steel consumption in PEB buildings is influenced by:
- Structural system selection
- Load assumptions
- Member sizing
- Connection detailing
- Span and bay planning
Even small inefficiencies in these areas can result in significant excess steel usage.
What Is Structural Design Optimization?
Structural design optimization is the process of:
- Achieving required structural performance
- Using the minimum amount of material
- Ensuring code compliance and safety
In PEB structures, optimization focuses on:
- Member geometry
- Stress distribution
- Load paths
- Fabrication efficiency
Why PEB Is Naturally Suited for Optimization
PEB systems are ideal for optimization because:
- They rely on software-driven analysis
- Members can be tapered or variable
- Loads are predictable
- Repetition allows refinement
Unlike conventional steel structures, PEB does not depend on uniform sections—every member is designed for actual demand.
Key Areas Where Optimization Reduces Steel Consumption
1. Tapered Built-Up Sections
Unlike hot-rolled uniform sections:
- PEB columns and rafters vary in depth
- Steel is provided only where stress demands it
This alone can reduce steel weight by 15–30%.
2. Accurate Load Assessment
Overestimated loads are the biggest cause of steel wastage.
Optimization ensures:
- Realistic live load values
- Correct wind load calculations
- Accurate seismic coefficients
Every unnecessary load increases member size and steel quantity.
3. Efficient Load Path Design
A clear load path:
- Reduces force concentration
- Eliminates redundant members
- Improves force distribution
Optimized load paths directly reduce steel tonnage.
4. Optimized Bay Spacing
Bay spacing affects:
- Member length
- Bending moments
- Steel quantity
Proper bay optimization balances:
- Structural efficiency
- Fabrication economy
- Architectural requirements
5. Bracing System Optimization
Efficient bracing:
- Reduces frame forces
- Minimizes column sizes
- Improves lateral stability
Choosing the right bracing configuration significantly reduces steel usage.
Role of Advanced Structural Analysis Software
Modern PEB optimization relies on:
- Finite element analysis
- Load combination automation
- Iterative member sizing
However, software alone does not optimize—engineering judgment does.
Connection Design and Steel Savings
Overdesigned connections lead to:
- Excess plate thickness
- Unnecessary stiffeners
- Increased fabrication cost
Optimized connection design:
- Matches force demand
- Reduces welding
- Improves constructability
Foundation Interaction and Steel Reduction
Reducing superstructure steel:
- Lowers foundation loads
- Reduces base plate sizes
- Optimizes anchor bolts
Optimization cascades benefits through the entire structure.
Optimization vs Overdesign
| Aspect | Overdesign | Optimization |
| Safety | Artificially high | Code-compliant |
| Steel usage | Excessive | Minimal |
| Cost | High | Efficient |
| Performance | Average | Improved |
Optimization does not reduce safety margins—it removes inefficiency.
Impact on Project Cost and Sustainability
Economic Benefits
- Lower steel procurement cost
- Reduced transportation and erection cost
- Smaller foundations
Environmental Benefits
- Reduced embodied carbon
- Lower resource extraction
- Sustainable construction practices
Common Mistakes That Increase Steel Consumption
- Conservative load assumptions
- Uniform section usage
- Ignoring secondary load paths
- Poor coordination between design and fabrication
Awareness of these mistakes is key to optimization.
Role of Structural Engineers in Steel Optimization
Structural engineers:
- Define load assumptions
- Control member sizing
- Ensure code compliance
- Balance safety and efficiency
At Rakhra Associates, optimization is driven by engineering clarity—not cost pressure.
Importance of Structural Audits in Optimized PEBs
Structural audits help:
- Verify design assumptions
- Identify overdesign
- Ensure long-term performance
Audits support optimization throughout the building’s lifecycle.
Indian Codes Supporting Optimized Steel Design
- IS 800 – Limit state design
- IS 875 – Accurate loading
- IS 1893 – Seismic efficiency
- NBC 2016 – Performance-based design
Codes allow optimization when applied correctly.
Future of Steel Optimization in PEB
By 2026 and beyond:
- AI-assisted optimization tools will increase
- Performance-based design will dominate
- Sustainability metrics will influence steel usage
Optimized steel design is becoming industry standard, not exception.
FAQs: Steel Optimization in PEB Structures
1. What is steel optimization in PEB?
Designing PEB structures using minimum steel without compromising safety.
2. How much steel can optimization save?
Typically 15–30%, depending on design.
3. Does optimization reduce safety?
No, it maintains code-required safety levels.
4. Is optimization only software-based?
No, engineering judgment is essential.
5. Why is overdesign common in steel structures?
Due to conservative assumptions and lack of optimization.
6. Can optimization reduce foundation size?
Yes, significantly.
7. Are tapered sections stronger?
They are more efficient, not weaker.
8. Does bay spacing affect steel quantity?
Yes, greatly.
9. Are optimized PEBs earthquake resistant?
Yes, when designed as per IS 1893.
10. Can optimization reduce erection time?
Yes, lighter members are easier to erect.
11. Is optimization suitable for industrial buildings?
Yes, especially industrial PEBs.
12. Does optimization increase design time?
Slightly, but saves construction time.
13. Can existing PEBs be optimized?
Through structural audits and retrofitting.
14. Is optimization sustainable?
Yes, it reduces embodied carbon.
15. Do Indian codes allow optimization?
Yes, under limit state design.
16. Can optimization affect architectural layout?
Usually no, structural changes are internal.
17. Is optimization useful for small PEBs?
Yes, every ton saved matters.
18. Does optimization reduce connection cost?
Yes, through accurate force design.
19. Is optimization different from value engineering?
Optimization is a key part of value engineering.
20. Who should perform steel optimization?
Qualified structural engineers.
Conclusion
Precise structural design optimization is the single most effective method to reduce steel consumption in Pre-Engineered Buildings. By focusing on accurate load assessment, efficient member design, and clear load paths, engineers can deliver structures that are safe, economical, and environmentally responsible.
At Rakhra Associates – Structural Engineers in Chandigarh, optimization is not viewed as an option—it is an essential part of responsible structural engineering, contributing to better performance, reduced costs, and sustainable construction practices.


