Blog
Smart Materials in Construction: The Future of Structural Engineering
Introduction: The Dawn of Smart Construction
The construction industry is undergoing a silent revolution. Traditional concrete, steel, and glass are giving way to smart materials — substances engineered to respond to environmental changes and structural stresses. These futuristic materials promise stronger, safer, and more sustainable buildings, aligning with the growing global emphasis on smart infrastructure.
For firms like Rakhra Associates, pioneers in structural engineering in Chandigarh, integrating smart materials into design and execution marks a shift toward efficiency, safety, and innovation.
What Are Smart Materials in Construction?
Smart materials are advanced substances that can sense and react to their surroundings. Unlike conventional materials that remain passive, these materials adapt dynamically to temperature, stress, moisture, or load changes, maintaining structural performance and integrity over time.
Common Categories of Smart Materials:
- Self-healing materials
- Shape-memory alloys
- Piezoelectric materials
- Thermochromic glass
- Carbon fiber-reinforced composites
- Photovoltaic (solar-responsive) materials
Each of these materials plays a role in making buildings more resilient, energy-efficient, and intelligent.
The Evolution of Materials in Structural Engineering
The journey from simple clay and lime to carbon nanocomposites reflects centuries of innovation. Early builders focused on durability, while modern engineers emphasize adaptability.
Smart materials now bridge these goals — offering durability and real-time responsiveness.
As Rakhra Associates highlights, structural engineering is no longer about static design; it’s about creating living structures that learn, adapt, and heal.
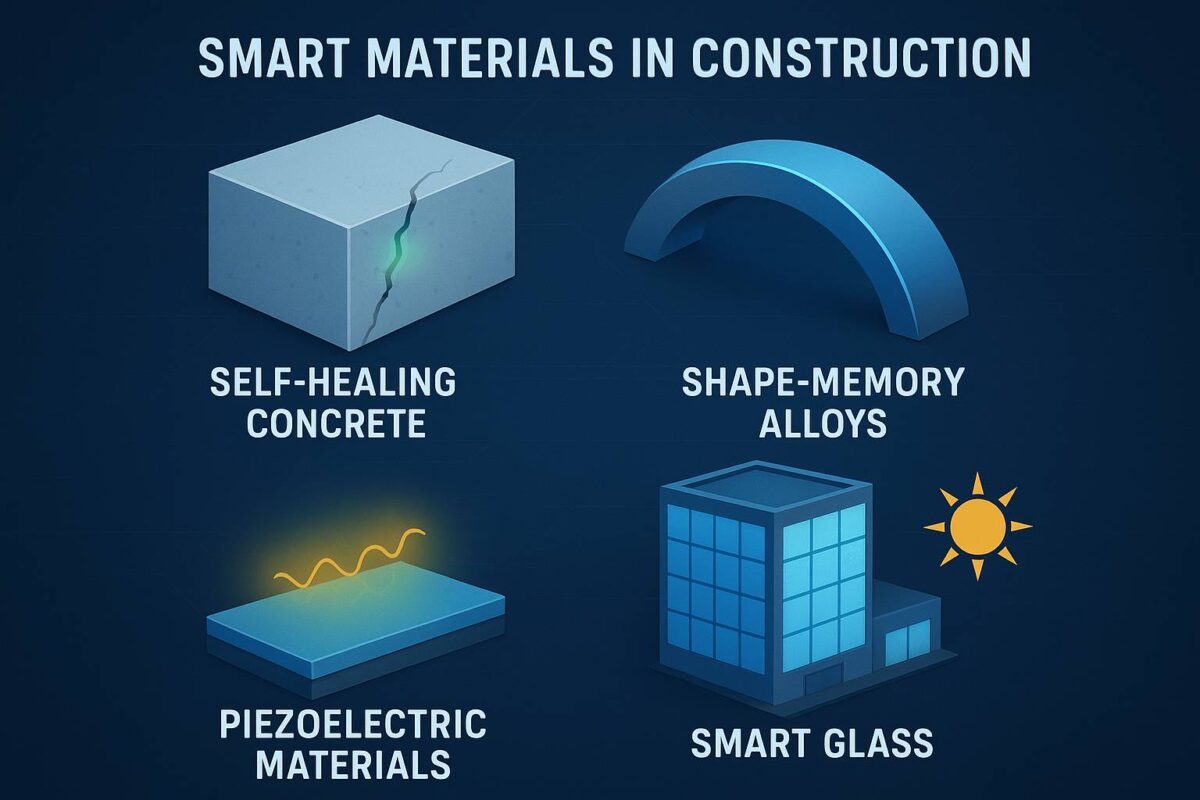
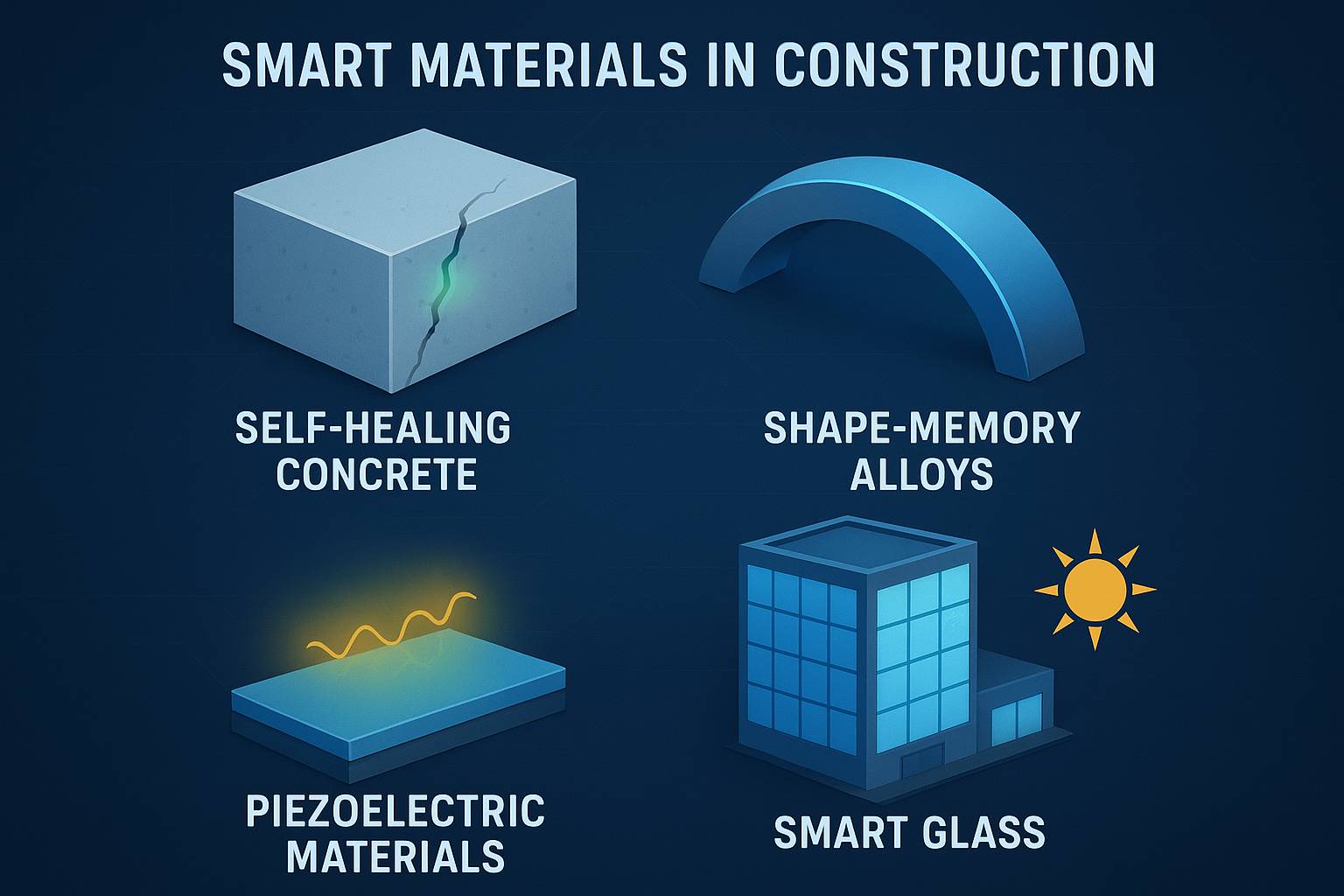
Types of Smart Materials and Their Applications
1. Self-Healing Concrete
One of the most groundbreaking materials in modern construction, self-healing concrete contains bacteria or polymers that activate when cracks form. Upon contact with moisture, these agents produce limestone, sealing the crack naturally.
Benefits:
- Extends lifespan by 30–50%
- Reduces maintenance costs
- Prevents water ingress and corrosion
Use Case: Bridges, tunnels, and water-retaining structures.
2. Shape-Memory Alloys (SMA)
SMAs, like Nitinol (Nickel-Titanium), can deform under stress but return to their original shape when heated. In structural applications, they help absorb seismic shocks and vibrations, making them ideal for earthquake-resistant buildings.
Rakhra Associates uses SMA-based dampers in high-rise structures across Chandigarh’s seismic zones.
3. Piezoelectric Materials
These materials generate electricity when subjected to pressure or vibration. When integrated into floors, roads, or walls, they can harvest energy from movement and convert it into usable power.
Application: Smart highways, kinetic floors, and vibration monitoring systems.
4. Thermochromic and Electrochromic Glass
Smart glass changes its transparency with temperature or electric current, reducing energy loads from air conditioning or lighting.
Advantages:
- Enhances energy efficiency
- Improves comfort and aesthetics
- Supports green building certifications
5. Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers (CFRP)
Lightweight yet stronger than steel, CFRP composites are used for retrofitting and strengthening existing structures. Their high tensile strength and corrosion resistance make them perfect for bridges, heritage buildings, and towers.
Smart Materials and Sustainability
Smart materials align perfectly with the global sustainability agenda. They reduce waste, cut down energy consumption, and extend the life of structures.
For example:
- Self-healing concrete minimizes CO₂ emissions by reducing cement demand.
- Smart glass lowers HVAC energy use by up to 25%.
- Piezoelectric floors generate renewable power in high-traffic zones.
As cities like Chandigarh move toward smart urban development, the role of such sustainable innovations becomes even more crucial.
Integration of Smart Materials in Structural Design
Incorporating smart materials requires advanced modeling, testing, and validation. Rakhra Associates employs BIM (Building Information Modeling) and Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to simulate how these materials behave under different environmental and loading conditions.
This ensures:
- Accurate material performance predictions
- Optimal cost-to-benefit ratios
- Compliance with national and international standards
Challenges in Adopting Smart Materials
While promising, these technologies face challenges:
- High initial costs compared to traditional materials
- Lack of standard codes for design and testing
- Limited local availability in emerging markets
- Knowledge gaps among construction teams
However, as adoption grows and costs drop, experts predict that smart materials will become standard practice in the next decade.
Smart Materials in Indian Context
India, with its diverse climate zones and growing infrastructure needs, stands to benefit immensely from smart materials.
From self-healing roads in Mumbai to solar-integrated facades in Gurgaon, projects are already proving their worth.
Rakhra Associates envisions introducing these materials into Chandigarh’s commercial and institutional developments — building structures that are not only strong but also self-sustaining and intelligent.
The Future of Structural Engineering
Tomorrow’s buildings won’t just stand tall—they’ll communicate, adapt, and regenerate. Structural elements will report stress levels, bridges will self-repair, and roads will power streetlights.
As artificial intelligence merges with material science, the line between engineering and biology will blur. Structures will become ecosystems — learning and evolving over time.
The Role of Rakhra Associates in the Smart Revolution
With decades of experience in structural design and material innovation, Rakhra Associates is spearheading the transition to smart construction practices in North India.
By adopting new technologies and research-driven engineering, the firm ensures that every project contributes to a smarter, greener, and safer built environment.
FAQs on Smart Materials in Construction
Q1. What makes a material “smart”?
Smart materials can sense environmental changes and respond by altering their physical properties, such as stiffness, shape, or color.
Q2. Are smart materials expensive?
Initially, yes. But they drastically reduce lifecycle costs by minimizing maintenance and extending structural lifespan.
Q3. Which smart material is most commonly used today?
Self-healing concrete and carbon-fiber composites are among the most adopted in large-scale infrastructure.
Q4. Can smart materials be used in existing structures?
Yes. Retrofitting with CFRP or smart coatings is a popular method to upgrade old structures.
Q5. Are there Indian standards for smart materials yet?
While BIS hasn’t formalized all smart material codes, guidelines exist under IS 456 and SP 34 for integrating new materials.
Q6. How is Rakhra Associates using these materials?
By incorporating smart composites and monitoring systems in new RCC projects and retrofits across Chandigarh.
Conclusion
Smart materials are more than technological novelties — they are the foundation of the next generation of construction. By merging adaptability with sustainability, they redefine what’s possible in structural engineering.
With visionary firms like Rakhra Associates leading the way, Chandigarh and India as a whole are on the brink of a smart construction era, where every structure is designed not just to last—but to think, adapt, and evolve. For more information watch our videos on Rakhra Associates Instagram Channel.