Blog
The Integration of PEB and RCC in Modern Construction
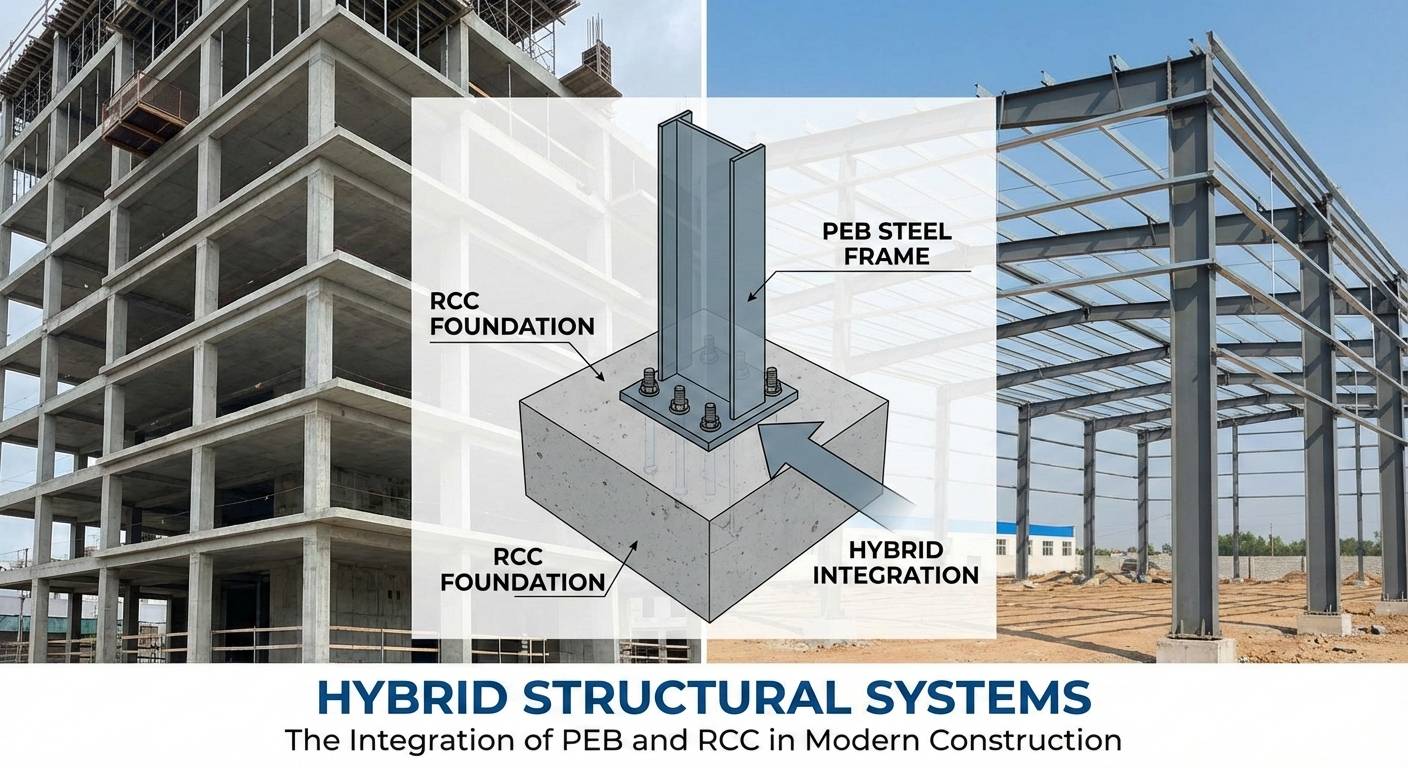
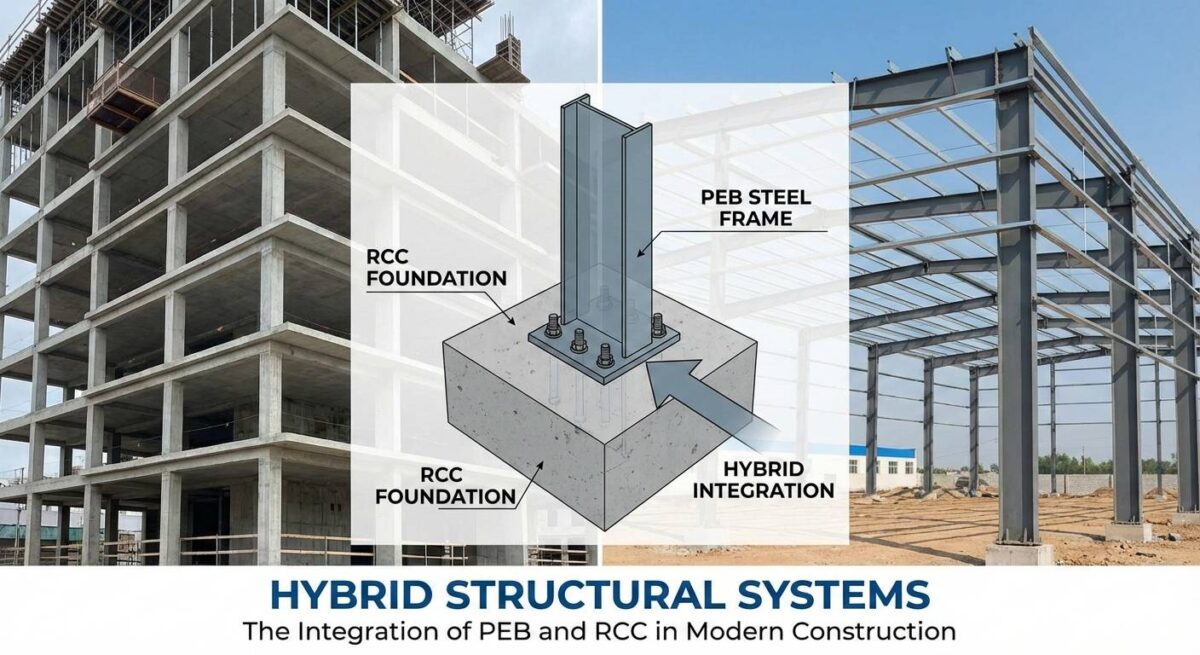
Modern construction is no longer limited to choosing between one structural system over another. Today’s buildings demand speed, strength, flexibility, cost efficiency, and long-term durability—all at the same time. This is where Hybrid Structural Systems, particularly the integration of Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEB) and Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC), are reshaping the future of construction.
At Rakhra Associates – Structural Engineers in Chandigarh, we believe awareness and technical clarity are as important as execution. This blog aims to explain what hybrid structural systems are, why they are increasingly used, how PEB and RCC work together, and where this approach makes the most sense, all in a simple, practical manner.
What Are Hybrid Structural Systems?
A hybrid structural system is a construction approach that combines two or more structural systems to utilize the best properties of each. In the Indian context, the most widely adopted hybrid combination is:
- RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) for foundations, cores, shear walls, and podiums
- PEB (Pre-Engineered Steel Structures) for superstructures, roofing, large spans, and lightweight framing
Instead of forcing one system to do everything, hybrid structures assign the right material to the right job.
Understanding RCC and PEB Individually
What is RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete)?
RCC is a composite material made of concrete and steel reinforcement. It is known for:
- High compressive strength
- Durability and fire resistance
Excellent performance in foundations and vertical load systems
RCC is commonly used in:
- Foundations
- Columns and beams
- Shear walls
- Staircases and lift cores
What is PEB (Pre-Engineered Building)?
PEB structures are factory-fabricated steel components designed using software and assembled at site. They offer:
- Lightweight construction
- Fast execution
- Large column-free spans
PEB is widely used for:
- Industrial sheds
- Warehouses
- Roof structures
- Auditoriums and hangars
Why Combine PEB and RCC?
No single structural system is perfect for all conditions. Hybrid systems emerge from engineering practicality, not trends.
Key Reasons for Integration
- Structural efficiency
- Cost optimization
- Speed of construction
- Seismic performance
- Architectural flexibility
- Load optimization
Hybrid systems allow engineers to balance strength and speed without compromising safety.
How Hybrid PEB–RCC Systems Work
A typical hybrid structure follows this logic:
- RCC foundation and substructure
Handles soil pressure, heavy loads, and long-term durability
- RCC cores or shear walls
Resist seismic and lateral forces
- PEB superstructure
Supports roofing, long spans, and lightweight floors - Steel–concrete connections
Carefully detailed to manage differential movement
This integration requires precise structural analysis and detailing, which is where experienced structural engineers play a critical role.
Structural Behavior of Hybrid Systems
Load Transfer Mechanism
- Vertical loads transfer from PEB members to RCC columns and foundations
- Lateral loads are shared between RCC shear elements and steel bracing
- Differential settlement is controlled through foundation design
Seismic Performance
Hybrid systems perform well in seismic zones when:
- RCC cores provide stiffness
- Steel frames provide ductility
- Connections are designed for energy dissipation
This balance is especially relevant for North Indian seismic zones, including Chandigarh and surrounding regions.
Where Hybrid Structural Systems Are Commonly Used
Industrial Buildings
- RCC foundations + PEB sheds
- Heavy machinery loads with wide clear spans
Commercial Complexes
- RCC basements + steel upper floors
- Faster construction with parking stability
Educational Institutions
- RCC cores + steel roof trusses
- Cost-effective expansion
Hospitals
- RCC for critical areas
- Steel for non-load-critical spaces
Mixed-Use Developments
- RCC podiums
- Steel upper structures
Advantages of Hybrid PEB–RCC Construction
Structural Advantages
- Improved seismic resistance
- Reduced dead load
- Better load distribution
Construction Advantages
- Faster project timelines
- Parallel fabrication and site work
- Reduced formwork requirements
Economic Advantages
- Optimized material usage
- Reduced foundation sizes
- Lower long-term maintenance
Architectural Advantages
- Large column-free spaces
- Flexible layouts
- Easier future modifications
Challenges in Hybrid Structural Systems
Despite their benefits, hybrid systems require careful planning.
Common Challenges
- Complex connection detailing
- Differential thermal expansion
- Coordination between civil and steel teams
- Quality control at interfaces
These challenges highlight the importance of experienced structural engineers and independent structural audits.
Role of Structural Engineers in Hybrid Design
Structural engineers are responsible for:
- System selection
- Load path clarity
- Connection design
- Seismic detailing
- Compliance with IS codes
At Rakhra Associates, hybrid systems are approached with engineering logic, not assumptions.
Indian Codes Relevant to Hybrid Structures
- IS 456 – RCC design
- IS 800 – Steel structures
- IS 1893 – Seismic analysis
- IS 875 – Load calculations
- NBC 2016 – Integrated safety provisions
Hybrid design demands cross-code compatibility, not isolated design.
Sustainability and Hybrid Construction
Hybrid systems contribute to sustainable construction by:
- Reducing concrete volume
- Minimizing material wastage
- Lowering embodied carbon
- Allowing reuse and dismantling
Steel recyclability and optimized RCC usage make hybrid buildings environmentally responsible.
Future of Hybrid Structural Systems in India
With increasing urban density and land costs:
- Hybrid systems will dominate commercial and industrial construction
- Modular + hybrid construction will grow
- Performance-based design will replace prescriptive approaches
Hybrid engineering is not a compromise—it is evolution.
FAQs – Hybrid Structural Systems (PEB + RCC)
1. What is a hybrid structural system in construction?
A system that combines RCC and steel structures to optimize performance.
2. Why are hybrid structures used instead of only RCC?
They improve speed, reduce weight, and enhance design flexibility.
3. Is PEB safe for multi-storey buildings?
Yes, when integrated properly with RCC cores and foundations.
4. Are hybrid buildings earthquake resistant?
They can perform very well when designed as per seismic codes.
5. What types of buildings benefit most from hybrid systems?
Industrial, commercial, hospitals, and large-span structures.
6. How does load transfer work in hybrid structures?
Loads move from steel to RCC elements through designed connections.
7. Is hybrid construction cost-effective?
Yes, due to optimized material usage and faster timelines.
8. Do hybrid structures require special foundations?
Foundations are usually RCC but optimized for lighter superstructures.
9. What is the lifespan of a hybrid building?
Comparable to RCC buildings when properly designed and maintained.
10. Are hybrid structures fire resistant?
Fire safety depends on fireproofing of steel and RCC protection.
11. Can hybrid systems be used in residential projects?
Yes, especially for villas, podiums, and community structures.
12. Do hybrid structures need more maintenance?
No, maintenance is comparable when detailing is done correctly.
13. What are common mistakes in hybrid construction?
Poor connection detailing and lack of coordination.
14. Is structural audit important for hybrid buildings?
Yes, audits ensure long-term safety and performance.
15. How does steel expansion affect RCC?
Expansion joints and detailing manage thermal effects.
16. Are hybrid systems approved by Indian codes?
Yes, when designed using relevant IS codes together.
17. Can old RCC buildings be converted to hybrid systems?
In many cases, yes—with proper structural evaluation.
18. Does hybrid construction reduce project time?
Significantly, due to off-site steel fabrication.
19. Is hybrid construction suitable for Chandigarh region?
Yes, especially considering seismic and soil conditions.
20. Who should design hybrid structural systems?
Qualified structural engineers with RCC and steel expertise.
Conclusion
Hybrid structural systems represent intelligent engineering, not trend-driven construction. By integrating PEB and RCC, modern buildings achieve the perfect balance of strength, speed, economy, and resilience.
At Rakhra Associates – Structural Engineers in Chandigarh, the focus remains on engineering awareness, safety, and long-term performance, ensuring that structures are not just built—but engineered responsibly.