Blog
Everything You Need to Know About Structural Stability Certificates in Chandigarh & Punjab
Introduction
In structural engineering, the load path and load transfer mechanisms are fundamental concepts that define the safety, strength, and functionality of any structure—from residential homes to multi-storey commercial towers. Yet, these terms are often misunderstood or overlooked, leading to design flaws, construction delays, or even structural failures.
At Rakhra Associates, one of the leading structural engineering consultancies in Chandigarh and North India, we believe in educating our clients, contractors, and fellow engineers about the critical principles that govern a building’s stability.
In this blog, we’ll walk you through what load path and load transfer mean, how they work, why they are crucial in design and construction, and how to ensure an efficient load transfer system in your project.
What is a Load Path in Structural Design?
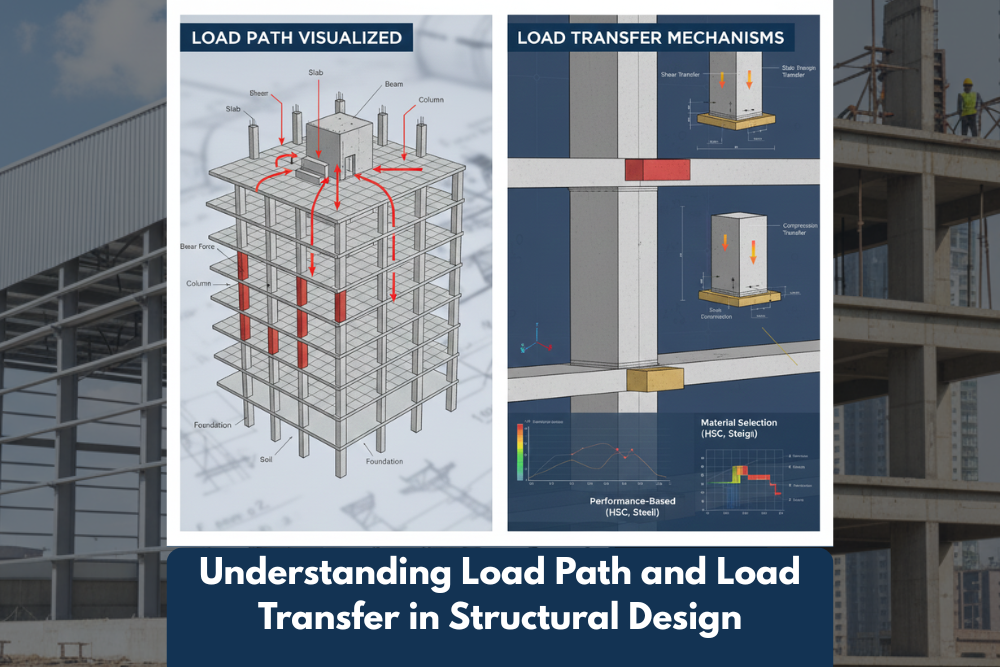
A load path is the route through which loads (forces or weights) move from the point of application (e.g., roof, floor, or occupancy) through various structural components and eventually down to the foundation and soil.
Think of it as the roadmap that guides how gravity, wind, seismic, or live loads travel through the structure.
Example:
For a multi-storey RCC building, the typical vertical load path is:
Slab → Beams → Columns → Foundation → Soil
For lateral loads (wind, seismic), the path may involve:
Roof → Bracings/Walls → Shear Walls/Frames → Foundation
Types of Loads in Structural Design
To understand load transfer, we must understand the types of loads structures are designed to resist:
- Dead Load (DL): Permanent static loads like self-weight of the structure, walls, finishes, etc.
- Live Load (LL): Temporary or movable loads like occupants, furniture, traffic, etc.
- Wind Load (WL): Lateral pressure due to wind.
- Seismic Load (EL): Earthquake-induced forces.
- Snow Load (SL), Thermal Loads, and Impact Loads in special structures.
Each of these loads follows a different load path depending on its direction, intensity, and point of application.
What is Load Transfer?
Load transfer refers to the actual process of transferring these loads from one structural component to the next until they safely reach the foundation.
It’s not just about direction but also how effectively and uniformly each member handles the load without failure, deflection, or overloading.
Load Transfer Mechanisms
1. Gravity Load Transfer (Vertical)
- Roof/Floor slab → Beam
- Beam → Column
- Column → Footing
- Footing → Soil
2. Lateral Load Transfer (Horizontal)
- Diaphragm (slabs) → Shear walls / Frames / Bracing
- Shear walls or braced frames → Foundation
3. Load Distribution Mechanisms
- One-way slabs: Load goes in one direction (to two beams)
- Two-way slabs: Load is shared in two perpendicular directions
- RCC Frame: Load is distributed to multiple members, offering redundancy
Understanding these mechanisms is crucial to ensure no member is overloaded or under-designed.
Importance of Load Path in Structural Design
A well-defined and uninterrupted load path is the backbone of a stable structure. Here's why it matters:
✅ Prevents Structural Failure
An unclear or broken load path can lead to progressive collapse, especially in earthquakes or extreme events.
✅ Optimizes Design Efficiency
Knowing how loads flow helps in material optimization, resulting in cost-effective designs.
✅ Compliance with IS Codes
Indian Standard Codes (IS 456 for RCC, IS 800 for Steel, IS 875 for loads, IS 1893 for seismic) require clear load transfer paths in design validation.
✅ Aids in Retrofitting and Modifications
In renovation or extension projects, engineers must understand existing load paths to prevent redistribution failures.
Load Path Disruptions: What Can Go Wrong?
Even small errors can severely disrupt load flow:
- Misaligned columns or beams
- Overcutting or coring in slabs for plumbing or HVAC
- Removal of a load-bearing wall
- Improperly placed openings near supports
- Inadequate lateral load resisting systems in seismic zones
At Rakhra Associates, we conduct detailed structural audits to ensure that the load path integrity remains intact in new and existing buildings.
Design Strategies to Ensure Efficient Load Transfer
1. Early Load Path Visualization
Structural engineers should map load paths during conceptual design, not just detailed engineering.
2. Vertical Alignment of Columns
Ensure that upper-storey columns align with lower ones to avoid transfer beams and reduce complexity.
3. Diaphragm Action in Floor Slabs
Design slabs to act as diaphragms to transfer lateral loads effectively.
4. Incorporate Redundancy
Design with alternative paths in mind—especially in seismic zones, where one path may fail.
5. Check Connection Details
Steel-to-concrete joints, bolted or welded connections, and rebar anchorage must be verified for effective transfer.
6. Use of Shear Walls or Bracing
For tall buildings, incorporate shear walls, moment frames, or bracings to resist lateral forces and distribute loads safely.
Indian Code Guidelines Relevant to Load Transfer
IS 875 (Part 1 to 5) – Loads on Buildings and Structures
IS 456:2000 – Design and construction of RCC elements
IS 1893:2016 – Criteria for Earthquake Resistant Design
IS 800:2007 – General construction in steel
Our team at Rakhra Associates ensures compliance with these codes while tailoring designs to local soil, climate, and seismic zone conditions in Punjab, Chandigarh, and adjoining states.
Load Transfer in Different Building Systems
| System | Load Path Feature |
| RCC Frame | Direct load transfer through beams and columns |
| Load-bearing Walls | Loads pass directly to walls and then foundations |
| Steel Frame | Relies on bolted/welded connections and bracings |
| PEB Structures | Load flows through frames, purlins, columns to anchor bolts |
| Composite Structures | Load transfer between different materials needs detailing |
Real-World Example from Rakhra Associates
In one of our multi-storey residential projects in Mohali, we encountered a design error from an earlier consultant where a key column was misaligned by 500 mm across three floors. Our team redesigned the load path using transfer beams and post-tensioned slabs, saving the client demolition costs while maintaining structural safety.
This is why understanding load path is not optional—it’s essential.
Conclusion
An uninterrupted, well-designed load path is fundamental to safe, cost-effective, and code-compliant construction. Whether you’re an architect, builder, or property owner, knowing how loads travel through your structure empowers better decisions at every stage—from design to construction and retrofitting.
At Rakhra Associates, we blend engineering expertise with cutting-edge tools to ensure your building is not just beautiful—but structurally sound from the ground up.















